Help
Why you need a lab assistant when you breadboard
Wiring your first physical breadboard is a frustrating experience. One wrong connection and the circuit does not work. Without an experienced lab or teaching assistant by your side, it is difficult to find out where is the mistake. Our breadboard simulator acts as a virtual and patient lab assistant who checks your every connection to help you gain experience and confidence to breadboard correctly.
Practice does not make perfect. Only perfect practice makes perfect - Vince Lombardi
You need to sign in with your Google account only if you wish to keep your completed wiring.
To complete wiring the breadboard
- Operate the switches in the circuit simulator. Read the description of the circuit for more information. The default circuit is the 1 to 2 demultiplexer. It is an easy circuit to understand and to breadboard.
- Using the circuit schematic, wire up the circuit in the breadboard simulator. When a wire end is placed in a socket of the breadboard that corresponds to a node on the schematic, the respective node of the schematic will turn red.
- If a correct connection is made, the wire ends will snap into the socket.
- When all the nodes are wired up, a red LED will light up near the VCC/GND terminals to indicate that the breadboard wiring is completed correctly.
- You may now operate the switches of the breadboard and observe the LED results.
Notes
- Click Help on menu to hide/show this Help panel. This site is optimised for computer browsers.
- All the VCC (red wire) and GND (black wire) connections are already done. When you wire up the actual circuit using the low cost Home Laboratory Kit, do remember to connect the VCC and GND wires.
- When you select a different schematic, the ones where you have completed the breadboard will be shown with a green background.
- The holes in the breadboard connected in blue are electrically connected.
- If you are unfamiliar with the breadboard, there are many resources available online that explains how they work. We recommend this quick Breadboard Infographic from Make Breadboarding Workshop or the longer Breadboard Tutorial from Science Buddies.
- Read Stony Brook University's paper that reports how their "virtual breadboard helped students to prepare for their labs, and significantly reduced the amount of time teaching assistants had to spend helping students in the actual lab."
Breadboard Simulator
Circuit Schematic & Simulator
24h Digital Clock Circuit Design Using 7493
This circuit shows the implementation of the hours portion of a 24H clock
The 4 blocks of a digital clock are
- 1 Hz clock generator to generate 1 PPS (pulse per second) signal to the seconds block.
- SECONDS block - contains a divide by 10 circuit followed by a divide by 6 circuit. Will generate a 1 PPM (pulse per minute) signal to the minutes block. The BCD outputs connect to the BCD to Seven Segment circuit to display the seconds values.
- MINUTES block - identical to the seconds block it contains 2 dividers; a divide by 10 followed by a divide by 6. Will generate a 1 PPH (pulse per hour) signal to the HOURS block. The BCD outputs connects to the BCD to Seven Segment circuit to display the minutes values.
- HOURS block - the 24hr clock will have a divide 24 counter. For 24H, it will count from 00 to 23 hexidecimal or 00 0000 to 10 0011 binary before resetting to 00 0000 and repeating. Click on SW7 and observe the LEDs.
- Notes:
- The ones circuit (IC1) is connected as a 4 bit ripple counter whereas the tens circuit (IC2) is connected as a 3 bit ripple counter. For IC2, the CLK signal is connected to CKB rather than CKA in IC1. We leave it to the reader to figure that if IC2 is connected as a 4 bit counter like IC1, the tens will increment by 2 rather than 1. Please see digital clock for more information on the 7493 connections.
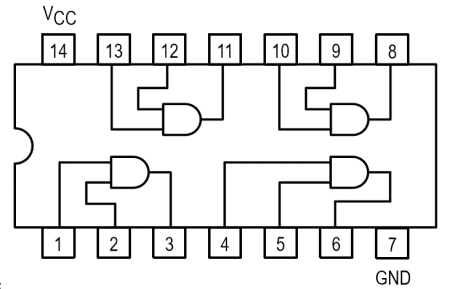
7408 Quad 2 Input AND Gate IC Pin Out
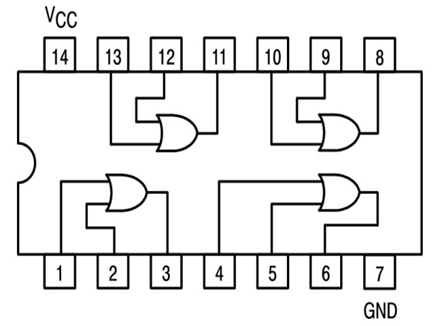
7432 OR Gate IC Pin Out
7493 4 Bit Binary Counter IC Pin Out
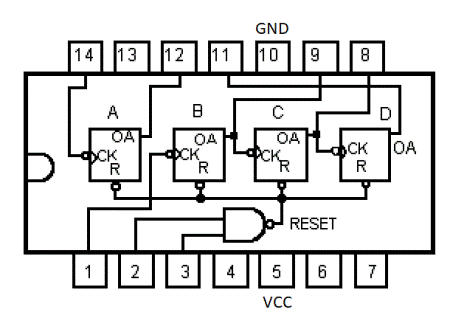
Note the VCC and GND Pins